Proportionate reductions in the forced expiratory volume in the first second (FEV1) and forced vital capacity (FVC) on spirometry, variably referred to in the medical literature as “restrictive”, “GOLD-unclassified”(1), “non-specific”(2), or Preserved Ratio Impaired Spirometry (PRISm)(3) patterns,
この部分
Respiratory Research201415:89
https://respiratory-research.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s12931-014-0089-y
Longitudinal Phenotypes and Mortality in Preserved Ratio Impaired Spirometry in the COPDGene Study
AJRCCM: American Journal of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine
https://www.atsjournals.org/doi/abs/10.1164/rccm.201804-0663OC?af=R
序文: 拘束性肺障害あるいはGOLDの分類不能スパイロメトリの代替名として知られているPreserved Ratio Impaired Spirometry (PRISm)の疾病罹患率と重要性は明確化に伴い、横断的リスク要素としての知識体として拡大しているが、縦断研究が少ない。
目的: PRISm現行喫煙・既往喫煙社の肺機能、レントゲン特性、死亡率の変化の縦断的パターン検証
方法: 現行・既往喫煙、45−80歳、 COPDGene (phase 1, 2008–2011)登録、5年間フォローアップにて再度検証 (phase 2, 2012–2016)
アンケート、スパイロメトリ、胸部CT、6分間歩行距離を両研究受診時施行
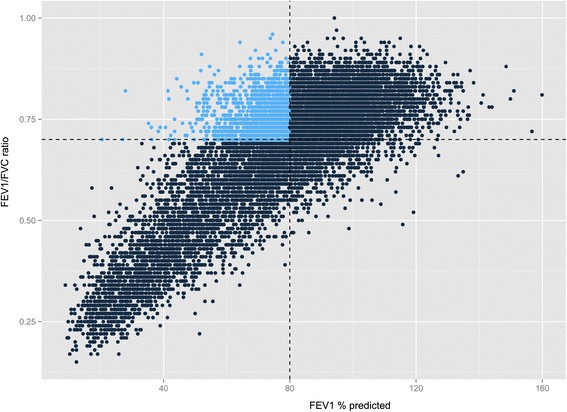
ベースライン特性、肺機能直軸変化、死亡罹を気管支拡張剤吸入後評価:: PRISm (FEV1/FVC < 0.7 and FEV1 < 80%), GOLD0 (FEV1/FVC > 0.7 and FEV1 > 80%)、GOLD1–4 (FEV1/FVC < 0.7)
測定項目と主な結果: PRISmの罹患率はphase 1とPhase 2と一致 (12.4–12.5%)
PRISm症例は肺機能カテゴリーへ移るか、他のカテゴリーからうつってきたものが一定数
Phase 1でのPRISm症例は、GOLD0へ移行:22.2%、GOLD1-4へ進行:25.1%
phase 1、phase 2ともにPRISmの症例では、 stable GOLD0 spirometryと比べ、FEV1減少率 (−27.3 ± 42.1 vs. −33.0 ± 41.7 ml/yr) 、正常CTでの比較a (51% vs. 52.7%)
逆に、PRISm発症で、肺機能減少加速
phase 1でのPRISmはGOLD0に比べ死亡率高度、GOLD1-4群に比べ相対的に低くはある
結論: PRISm罹病率は高く、死亡率増加と相関、他の病相へ(から)の移行状態が存在。長軸的変化(進行)特性について注目が必要。
